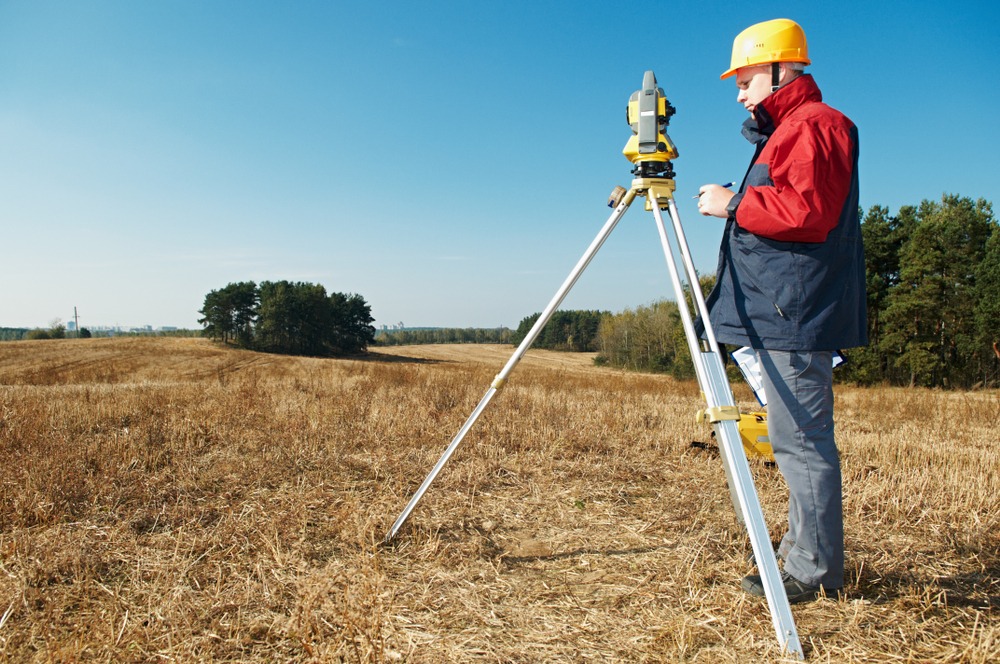
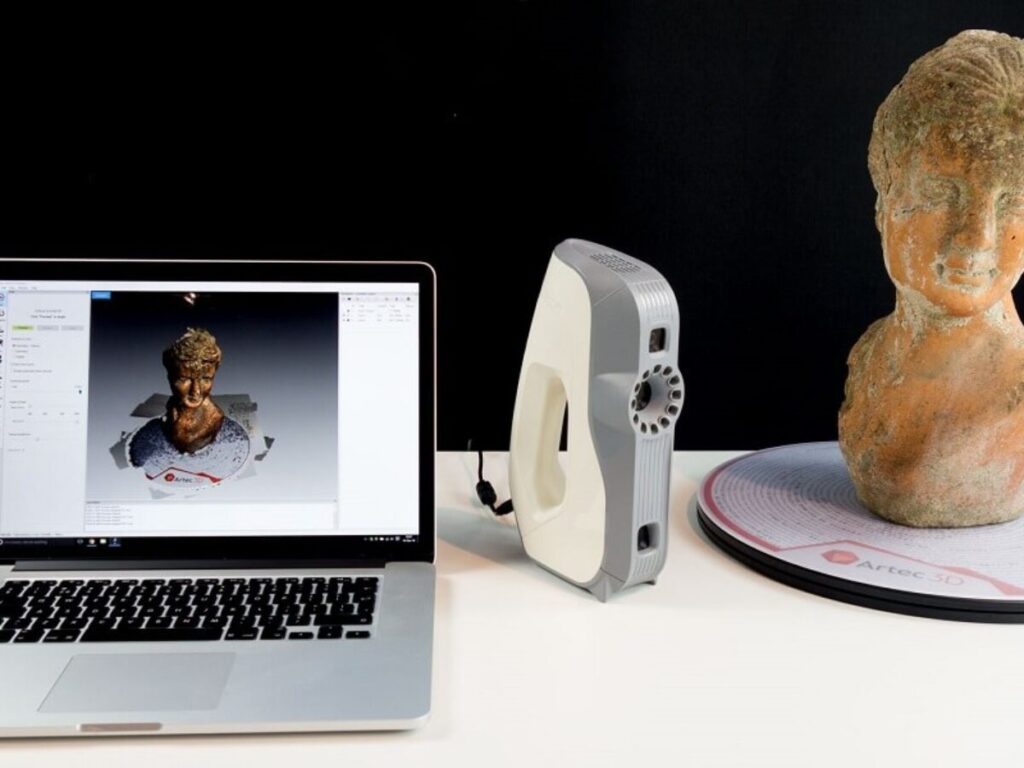
High definition is surveying-also known as 3D laser surveying-is well known for the benefits that it brings to manufacturing companies. However, there are some manufacturing companies-typically small to midsized companies that still use traditional surveying methods in an attempt to cut costs. Unfortunately, using older surveying methods rarely results in lower surveying costs. It usually results in higher costs than companies would pay if they hired a 3D surveying service.
Whereas traditional surveying methods require prolonged involvement by the surveyor and commonly yield less than accurate results, laser surveying-also known as laser scanning-reduces the cost of surveying by offering accurate results in as little as one surveying session. When companies use laser scanning, they can view an object’s data results according to three basic data models: polygon mesh models, which are typically used to conceptualize an object; surface models, which are used to model the surface of an object; and solid CAD models, which are used to incorporate design intent and can be directly manufactured from.
Regardless of which scanning application meets your company’s needs, laser scanning can improve your company’s product quality, shorten its production cycles and increase its manufacturing efficiency. In many cases, long production cycles, low manufacturing efficiency, and mediocre product quality are based on nothing more than inaccurate data produced by traditional surveying methods.
The product defects that result from this inaccuracy remain hidden from the naked eye and are impossible to detect with analog and GPS technology. But laser scanning offers quality inspection modules, such as colormap deviation, cross-section analysis, and geometric dimensioning and tolerancing, that reveal defects that result from the following flaws, among others: thickness deviation, boundary deviation, reference geometry deviation, and virtual edge deviation.
If you have ever purchased a product whose inner workings experienced significant wear in a short period or a product whose covering, lid, door, or attachment pieces didn’t conform to their settings, you probably purchased a product that didn’t benefit from high-definition surveying. Products that contain the deviations mentioned above don’t always malfunction, but they do present as consumer-unfriendly products that can poison consumers’ perception of a certain brand, regardless of its future quality.
If this is something that your company can’t afford, then it’s time to take a look at how laser scanning can benefit your manufacturing process at an affordable price. To increase the quality of your products and the efficiency of your manufacturing process, contact a high-definition surveying company to hear how you can benefit from high-definition surveying today.